Problem Formulation
Consider the following minimal example where a TypeError: 'bool' object is not subscriptable occurs:
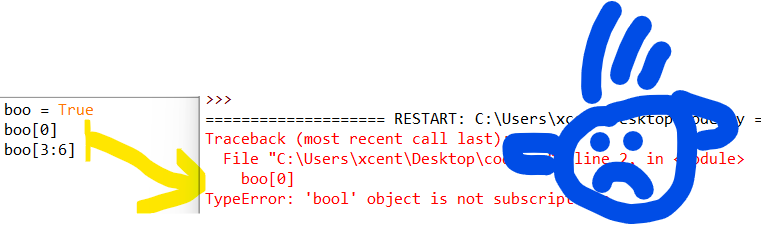
boo = True boo[0] # or: boo[3:6]
This yields the following output:
♥️ Info: Are you AI curious but you still have to create real impactful projects? Join our official AI builder club on Skool (only $5): SHIP! - One Project Per Month
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "C:\Users\xcent\Desktop\code.py", line 2, in <module>
boo[0]
TypeError: 'bool' object is not subscriptableSolution Overview
Python raises the TypeError: 'bool' object is not subscriptable if you use indexing or slicing with the square bracket notation on a Boolean variable. However, the Boolean type is not indexable and you cannot slice it—it’s not iterable!
In other words, the Boolean class doesn’t define the __getitem__() method.
boo = True boo[0] # Error! boo[3:6] # Error! boo[-1] # Error! boo[:] # Error!
You can fix this error by
- converting the Boolean to a string using the
str()function because strings are subscriptable, - removing the indexing or slicing call,
- defining a dummy
__getitem__()method for a custom “Boolean wrapper class”.
🌍 Related Tutorials: Check out our tutorials on indexing and slicing on the Finxter blog to improve your skills!
Method 1: Convert Boolean to a String
If you want to access individual characters of the “Boolean” strings "True" and "False", consider converting the Boolean to a string using the str() built-in function. A string is subscriptable so the error will not occur when trying to index or slice the converted string.
boo = True boo_string = str(boo) print(boo_string[0]) # T print(boo_string[1:-1]) # ru
Method 2: Put Boolean Into List
A simple way to resolve this error is to put the Boolean into a list that is subscriptable—that is you can use indexing or slicing on lists that define the __getitem__() magic method.
bools = [True, True, True, False, False, False, True, False] print(bools[-1]) # False print(bools[3:-3]) # [False, False]
Method 3: Define the __getitem__() Magic Method
You can also define your own wrapper type around the Boolean variable that defines a dunder method for __getitem__() so that every indexing or slicing operation returns a specified value as defined in the dunder method.
class MyBool:
def __init__(self, boo):
self.boo = boo
def __getitem__(self, index):
return self.boo
my_boolean = MyBool(True)
print(my_boolean[0])
# True
print(my_boolean[:-1])
# True
This hack is generally not recommended, I included it just for comprehensibility and to teach you something new. 😉
Summary
The error message “TypeError: 'boolean' object is not subscriptable” happens if you access a boolean boo like a list such as boo[0] or boo[1:4]. To solve this error, avoid using slicing or indexing on a Boolean or use a subscriptable object such as lists or strings.
